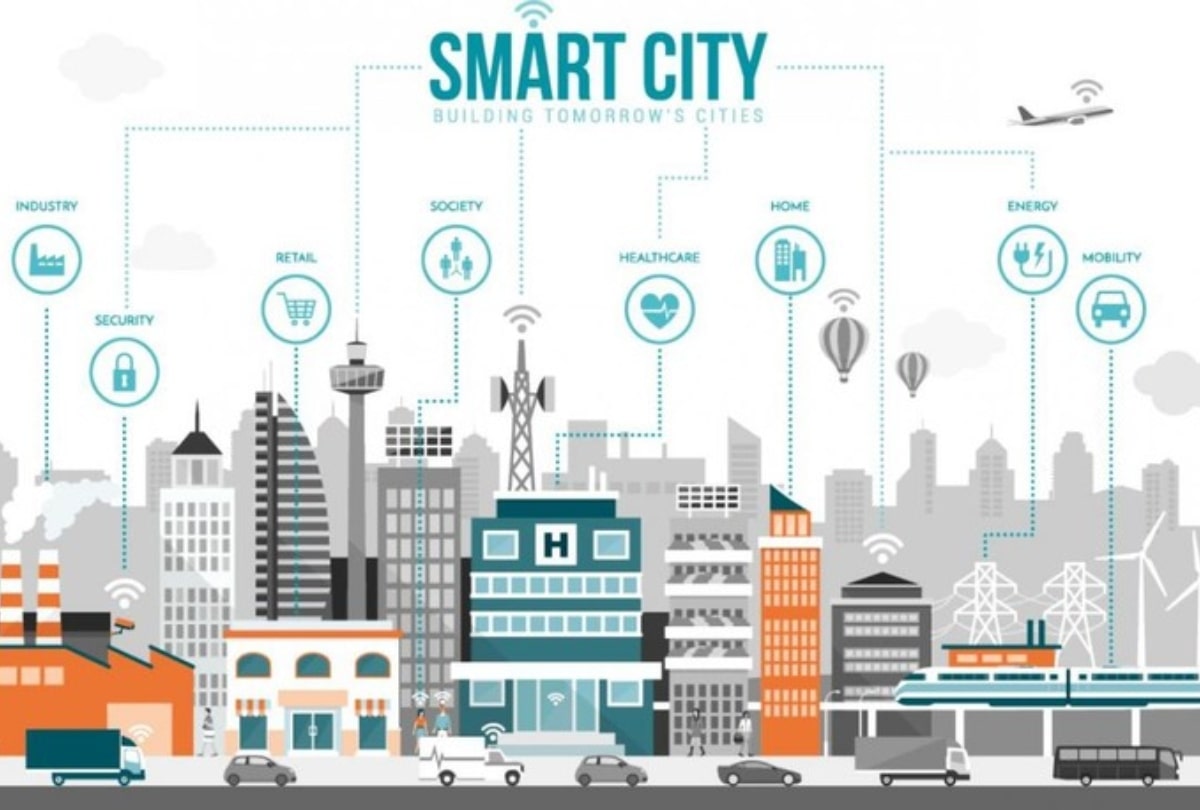
In the ever-evolving world of digital technology, two innovations stand out as true game-changers: 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). While each is impressive on its own, the combination of these technologies is set to transform our world in ways we’re only beginning to imagine.
This comprehensive guide explores how 5G technology is enhancing and revolutionizing the Internet of Things, opening up new possibilities and reshaping industries across the globe.
Understanding the Basics: 5G and IoT
Before diving into the exciting ways 5G is enhancing IoT, let’s understand what these technologies are and why they’re so important.
What is 5G?
5G, or fifth-generation cellular network technology, is the latest iteration of mobile network standards. It’s designed to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity compared to its predecessors. 5G isn’t just an incremental improvement over 4G; it’s a quantum leap that promises to enable a wide range of new applications and services.
Key features of 5G include:
- Extremely high data rates (up to 20 Gbps)
- Ultra-low latency (as low as 1 millisecond)
- Massive device connectivity (up to 1 million devices per square kilometer)
- Enhanced reliability and availability
- Improved energy efficiency
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things refers to the vast network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity, which enables these objects to collect and exchange data. IoT has the potential to make our lives more convenient, efficient, and connected.
Examples of IoT devices include:
- Smart home devices (thermostats, security cameras, lighting systems)
- Wearable Technology (fitness trackers, smartwatches)
- Connected vehicles
- Industrial sensors and monitoring equipment
- Smart city infrastructure (traffic lights, waste management systems)
The Perfect Match: How 5G Complements IoT
5G and IoT are a match made in digital heaven. The capabilities of 5G address many of the limitations that have held back the full potential of IoT. Here’s how:
Increased Speed and Bandwidth
One of the most obvious benefits of 5G for IoT is its dramatically increased speed and bandwidth. With theoretical peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, 5G can handle the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices with ease.
This increased speed and bandwidth enable:
- Real-time data processing and analysis
- High-quality video streaming from IoT devices
- Faster firmware and software updates for IoT devices
- Support for more data-intensive IoT applications
For example, in a smart city context, 5G can enable the simultaneous transmission of high-definition video feeds from thousands of security cameras, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis of traffic patterns, public safety, and more.
Ultra-Low Latency
Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from its source to its destination. 5G promises latency as low as 1 millisecond, which is a significant improvement over 4G’s average latency of 20-30 milliseconds.
This ultra-low latency is crucial for IoT applications that require real-time responsiveness, such as:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Remote surgery and telemedicine
- Industrial automation and robotics
- Virtual and augmented reality experiences
Imagine a network of self-driving cars communicating with each other and with traffic infrastructure in real-time, making split-second decisions to avoid accidents and optimize traffic flow. This level of responsiveness is only possible with the ultra-low latency of 5G.
Massive Device Connectivity
5G is designed to support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer, a massive increase over 4G’s capacity. This capability is essential for the widespread adoption of IoT, as the number of connected devices is expected to reach 75 billion by 2025.
This increased connectivity enables:
- Large-scale IoT deployments in smart cities
- Dense sensor networks in industrial settings
- Widespread adoption of consumer IoT devices
- Efficient management of smart grids and utilities
For instance, a smart factory could deploy thousands of sensors to monitor every aspect of its operations, from equipment performance to environmental conditions, all communicating in real-time over a 5G network.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is a key feature of 5G that allows for the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This enables network operators to allocate resources more efficiently and provide customized services for different IoT applications.
Benefits of network slicing for IoT include:
- Dedicated bandwidth for critical IoT applications
- Improved quality of service for specific IoT use cases
- Enhanced security through isolation of different IoT networks
- Flexible and scalable network management
For example, a hospital could have a dedicated network slice for its IoT medical devices, ensuring they always have the necessary bandwidth and security, while another slice could be used for less critical applications like visitor Wi-Fi.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Many IoT devices operate on battery power, making energy efficiency crucial. 5G is designed to be more energy-efficient than previous generations, which can significantly extend the battery life of IoT devices.
This improved energy efficiency enables:
- Longer-lasting IoT sensors and devices
- Reduced maintenance costs for IoT deployments
- IoT applications in remote or hard-to-reach locations
- More sustainable and environmentally friendly IoT solutions
Imagine environmental sensors deployed in a vast forest to monitor wildlife and detect early signs of wildfires. With 5G’s energy efficiency, these sensors could operate for years without needing battery replacement.
Transforming Industries with 5G-Enabled IoT
The combination of 5G and IoT is set to revolutionize various industries. Let’s explore some of the most significant impacts:
Healthcare
5G-enabled IoT is poised to transform healthcare in numerous ways:
- Remote patient monitoring with real-time data transmission
- Telemedicine with high-quality video consultations
- IoT-enabled drug delivery and management systems
- AI-powered diagnostics using data from wearable devices
- Augmented reality-assisted surgeries
For instance, a patient with a chronic condition could have their vital signs continuously monitored by IoT devices, with data transmitted in real-time over 5G to their healthcare provider. Any concerning changes could trigger immediate alerts, potentially saving lives.
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
The industrial sector stands to benefit greatly from 5G-enhanced IoT:
- Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of equipment
- Augmented reality for training and maintenance procedures
- Autonomous robots and vehicles in factory settings
- Digital twins for complex system modeling and optimization
- Enhanced supply chain visibility and management
A 5G-connected factory could use thousands of IoT sensors to monitor every aspect of production, from machine performance to environmental conditions. This data could be analyzed in real-time to optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
5G and IoT are key enablers for the smart cities of the future:
- Intelligent traffic management systems
- Smart energy grids for efficient power distribution
- Waste management optimization
- Environmental monitoring and pollution control
- Enhanced public safety through connected surveillance systems
Imagine a city where traffic lights automatically adjust based on real-time traffic data, where waste bins signal when they need to be emptied, and where air quality is continuously monitored and managed. 5G-enabled IoT makes all of this possible.
Agriculture
The agricultural sector can leverage 5G and IoT for precision farming:
- Soil and crop monitoring with distributed sensors
- Automated irrigation systems
- Livestock tracking and health monitoring
- Drone-based crop surveillance and treatment
- Autonomous farming equipment
Farmers could use networks of IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health, with data transmitted over 5G networks. This information could then be used to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to increased yields and more sustainable farming practices.
Automotive and Transportation
5G and IoT are set to revolutionize how we move:
- Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication for improved safety
- Real-time traffic and navigation updates
- Autonomous vehicle coordination and control
- Predictive maintenance for vehicles and infrastructure
- Enhanced fleet management for logistics companies
With 5G, vehicles could communicate with each other and with road infrastructure in real-time, enabling safer and more efficient transportation. Autonomous vehicles could coordinate their movements, reducing traffic congestion and improving road safety.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of 5G-enhanced IoT is enormous, there are several challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
Security and Privacy
With billions of connected devices transmitting sensitive data, security and privacy become paramount concerns. 5G’s improved security features, such as enhanced encryption and network slicing, can help address these issues, but ongoing vigilance and innovation in cybersecurity will be crucial.
Infrastructure Development
Rolling out 5G infrastructure, especially in rural or developing areas, is a significant challenge. The high-frequency signals used by 5G have shorter ranges and are more easily blocked by obstacles, requiring a denser network of base stations.
Standardization and Interoperability
As the IoT ecosystem grows, ensuring interoperability between devices from different manufacturers becomes increasingly important. Industry-wide standards for 5G IoT communication will be necessary to realize the full potential of this technology combination.
Spectrum Allocation
The radio frequency spectrum is a finite resource, and allocating sufficient bandwidth for 5G while accommodating existing services is a complex regulatory challenge.
Energy Consumption
While 5G is more energy-efficient on a per-bit basis, the massive increase in data transmission could lead to higher overall energy consumption. Balancing the benefits of 5G-enabled IoT with environmental concerns will be an ongoing challenge.
The Future of 5G and IoT
As 5G networks continue to roll out globally and IoT devices become increasingly sophisticated, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and use cases emerge. Some exciting possibilities include:
Edge Computing and AI
The combination of 5G, IoT, edge computing, and artificial intelligence will enable real-time data processing and decision-making at the edge of the network. This could lead to more responsive and intelligent IoT systems across various industries.
Extended Reality (XR)
5G’s high bandwidth and low latency make it ideal for extended reality applications, including virtual, augmented, and mixed reality. We can expect to see more immersive IoT experiences in fields like education, entertainment, and industrial training.
Tactile Internet
The ultra-low latency of 5G could enable the “tactile internet,” allowing for the real-time transmission of touch and motion. This could revolutionize fields like remote surgery, industrial automation, and virtual reality.
Swarm Robotics
5G’s ability to connect massive numbers of devices could enable large-scale deployments of small, cooperative robots. These could be used for tasks like environmental monitoring, search and rescue operations, or precision agriculture.
Conclusion
The marriage of 5G technology and the Internet of Things is ushering in a new era of connectivity, efficiency, and innovation. From smart cities and autonomous vehicles to precision agriculture and advanced healthcare, the applications of 5G-enhanced IoT are vast and transformative.
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide, 5G addresses many of the limitations that have held back the full potential of IoT. Its increased speed, ultra-low latency, massive device connectivity, and improved energy efficiency are enabling new use cases and enhancing existing ones across various industries.
However, realizing the full potential of 5G-enabled IoT will require overcoming challenges related to security, infrastructure development, standardization, and energy consumption. As these challenges are addressed and the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful applications emerge.
The future of 5G and IoT is bright, promising a world that is more connected, efficient, and responsive to our needs. As this technology continues to develop and deploy, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping our digital future. Whether you’re a technology enthusiast, a business leader, or simply curious about the future of connectivity, keeping an eye on the evolving landscape of 5G and IoT will be essential in the coming years.